
杜宇慧个人网页---智能医学图像分析
地址:中国, 太原
杜宇慧教授首篇Essential Science Indicators高被引论文问世
时间:2019-06-12 19:37:30 来源: 点击:[1320]
智能医学图像分析实验室导师杜宇慧教授以第一作者在2016年1月份出版的论文《Interaction among subsystems within default mode network diminished in schizophrenia patients: a dynamic connectivity approach》日前成为Essential Science Indicators高被引论文,该论文发表于Schizophrenia Research,被引频次65次,在Web of Science 中的使用次数为44次,且该论文入选动态脑功能网络研究前沿(Research Front)论文。
该论文发现健康对照受试者在反映默认模式网络(DMN)前后子网络之间更强连通性的状态下花费更多时间,而精神分裂症患者在断开连接的DMN状态下花费更多时间这一重要发现(见图)。大量的高水平文章引用了作者在动态脑功能网络研究方面的成果,这些文章包括发表于NeuroImage的“The dynamic functional connectome: State-of-the-art and perspectives”、“The energy landscape underpinning module dynamics in the human brain connectome”、“Fast imaging for mapping dynamic networks”、发表于Neuro杂志的 “From Maps to Multi-dimensional Network Mechanisms of Mental Disorders” 等。
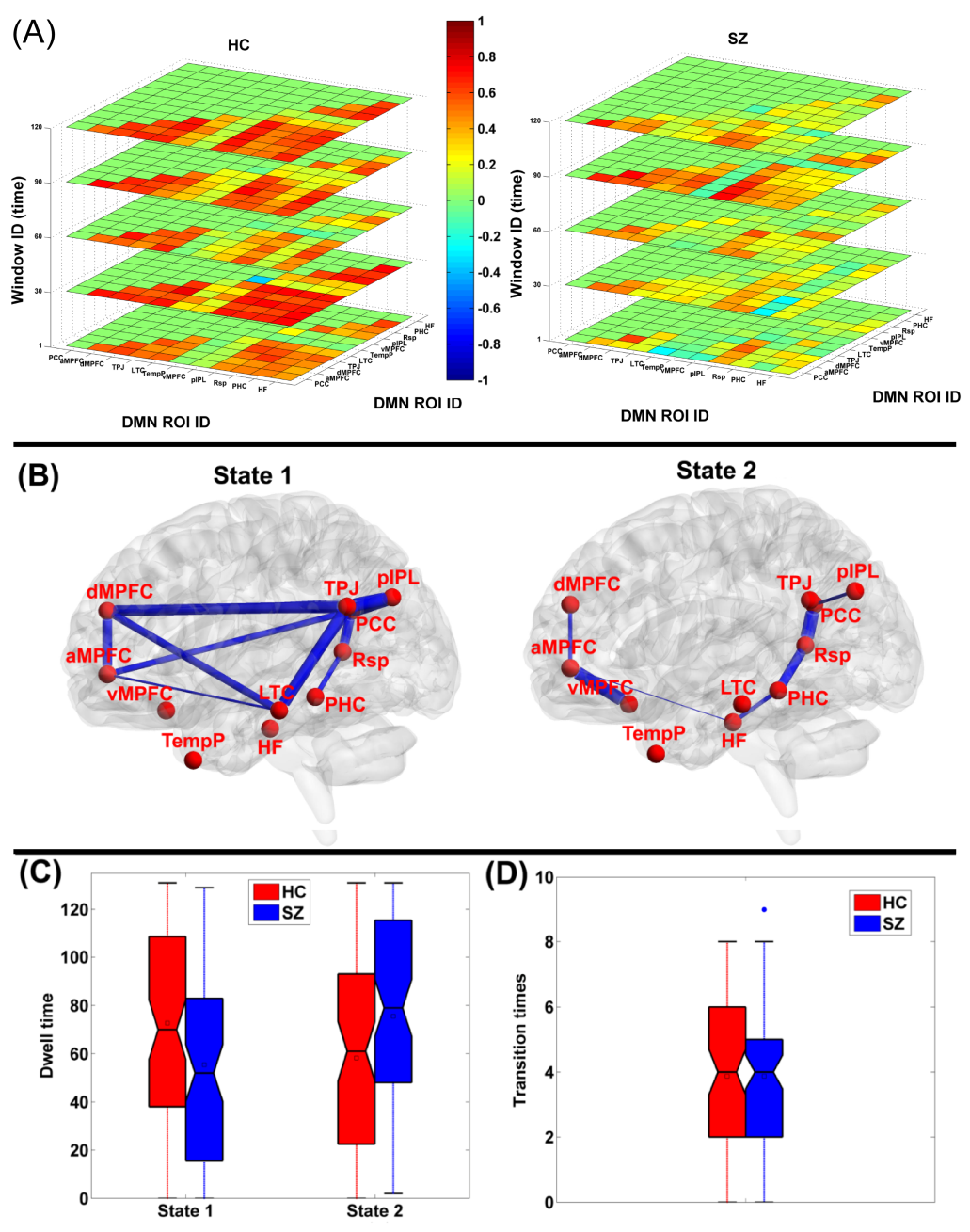
图 (A)动态功能连接。(B)提取的连接状态1和2。(C)每个受试者在不同连接状态中的停留时间,用HC组(红色)和SZ患者组(蓝色)的箱线图显示。(D)每个受试者的状态间转变时间。
摘要
Default mode network (DMN) has been reported altered in schizophrenia (SZ) using static connectivity analysis. However, the studies on dynamic characteristics of DMN in SZ are still limited. In this work, we compare dynamic connectivity within DMN between 82 healthy controls (HC) and 82 SZ patients using resting-state fMRI. Firstly, dynamic DMN was computed using a sliding time window method for each subject. Then, the overall connectivity strengths were compared between two groups. Furthermore, we estimated functional connectivity states using K-means clustering, and then investigated group differences with respect to the connectivity strengths in states, the dwell time in each state, and the transition times between states. Finally, graph metrics of time-varying connectivity patterns and connectivity states were assessed. Results suggest that measured by the overall connectivity, HC showed stronger inter-subsystem interaction than patients. Compared to HC, patients spent more time in the states with nodes sparsely connected. For each state, SZ patients presented relatively weaker connectivity strengths mainly in inter-subsystem. Patients also exhibited lower values in averaged node strength, clustering coefficient, global efficiency, and local efficiency than HC. In summary, our findings indicate that SZ show impaired interaction among DMN subsystems, with a reduced central role for posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) and anterior medial prefrontal cortex (aMPFC) hubs as well as weaker interaction between dorsal medial prefrontal cortex (dMPFC) subsystem and medial temporal lobe (MTL) subsystem. For SZ, decreased integration of DMN may be associated with impaired ability in making self-other distinctions and coordinating present mental states with episodic decisions about future.
智能医学图像分析实验室
2019年6月12日

 您当前的位置:
您当前的位置: